High blood pressure symptoms (signs)
- Headache, tightness, especially in the back of the head and temples;
- noise and tinnitus;
- "spot", spot, a veil in front of the eyes;
- decreased vision;
- Deterioration of spatial coordination and fine motor skills;
- Tremors, numbness in arms and legs;
- Nausea and vomiting.
- I - blood pressure reading 140-160 per 90-100 mmHg;
- II-Pressure 160-180 per 100-110 mm Hg;
- III - When the upper limit of the second stage is exceeded.
causes of high blood pressure
- kidney disease;
- Vascular Pathology;
- Renal artery obstruction;
- Thyroid pathology;
- Adrenal gland dysfunction;
- Smoking and drinking;
- Insufficient or excessive physical activity.
- Aged over 55 years old;
- obesity;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- genetic predisposition;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- Feeling frequently stressed and depressed.
Which doctor should I contact?
- What symptoms are you worried about?
- How long ago did they begin to appear?
- How often do high blood pressure attacks occur?
- Are they related to any external factors?
- Does the patient have heart, kidney, or endocrine disease?
- What kind of life does he lead?
- What symptomatic treatment does he use to treat his attacks?
ways to treat disease
- Control weight through diet;
- engage in physical exercise of varying intensities;
- taking diuretic medications;
- use of antitachycardia drugs;
- Taking adrenergic blocking agents;
- Use antispasmodics and analgesics;
- Use potassium-containing medications.
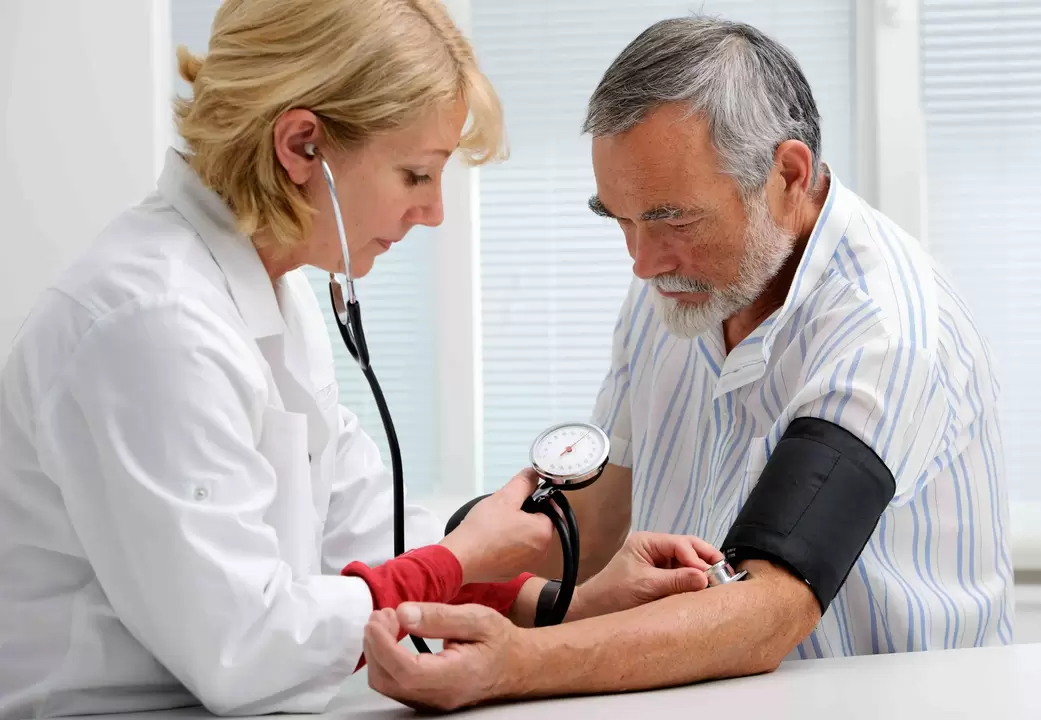
Diagnosis of high blood pressure
- Repeat blood pressure measurements. Perform on both arms, in a seated or standing position, depending on age. The accuracy is about 85%.
- Daily pressure monitoring is a program that allows continuous monitoring over a specified period of time using a portable device. The cost depends on the required duration of monitoring. The accuracy rate exceeds 95%.
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood. Determine the quantitative and qualitative composition of fluids and the rates of chemical reactions in the body. The accuracy is about 75%.
- Chest X-ray. Allows you to visually assess your heart condition. Accuracy - less than 70%.
Possible complications
- deformation of blood vessels;
- coronary heart disease;
- kidney disease;
- the threat of stroke and heart attack;
- Blurred vision due to damage to blood vessels in the eye;
- The development of "lung heart";
- Exercise intolerance.
High-risk groups
- People with weight gain and obesity;
- Those whose activities are associated with strenuous physical activity or, conversely, lack of physical activity;
- People with a genetic predisposition to high blood pressure;
- Living in a polluted area;
- smokers and alcoholics;
- People who do not monitor the fat and carbohydrate content of their food;
- People diagnosed with serious heart, liver or kidney disease.
Prevent high blood pressure
- Prompt treatment of all conditions that cause high blood pressure - heart, blood vessels, blood, kidneys;
- Stick to a daily routine;
- Avoid sleep deprivation and overexertion;
- Maintain a healthy diet - avoid foods high in fat and cholesterol, alcoholic beverages, strong tea and coffee;
- Engage in moderate physical activity and avoid a sedentary lifestyle;
- Conduct regular preventive inspections;
- Take a vitamin and mineral complex recommended by your doctor to stay healthy.